THE gSes system
GSES meta standard
GSES Meta Standard
The GSES Meta Standard is a universal sustainability rating system for companies, public organizations and NGOs. The rating works with internationally accepted frame-works and standards such as; GRI, SASB Standards, ISO, and over 550 ecolabels and certification schemes and integrates them in standard and platform. The standard is measuring on: CSR, Health & Safety, Circular Economy, Biodiversity, Sustainable Procurement on organization and product/asset level.
THE GSES SYSTEM
The overall structure of the GSES System
We identified all global ecolabels and certificates that relate to sustainability and ESG. Then, we checked them on the KPI’s they actually measure, the sustainability topics they consider, and how are they are verified.
From these, we created the meta standard based on all the certificates and frameworks that already exist, to make reporting and. verification easy and cost-efficient.
In the GSES system, these KPI’s are benchmarked against the overarching certification schemes of the GSES System pillars on the organization level. The college of experts and technical committee are responsible for the benchmarking of every KPI measured in a certification scheme to the guides and controls of the overarching certification schemes of the GSES System pillars.
Therefore, if a company already has a certification it is rewarded by not having to re-audit the KPI’s it is already in compliance with from its certifications.
If the company does not have any certifications or labels, the GSES pillar benchmark comes in. This is done in three simple steps: 1. Filling in the digital assessments on the GSES platform per sustainability pillar, 2. Uploading the required evidence required and 3. Requesting an audit by an independent certification institution.
Ready to be sustainable?
The overarching assessments of the GSES System pillars are based on well-recognized, pre-existing frameworks, certification schemes and ecolabels, such as the ISO guidelines and standards, the GRI, and over 550 certificates and ecolabels.
THE gSes system
The Certification/exemption levels
The GSES Meta Standard considers certifications as exemptions, on 2 levels: 1st and 2nd line.
1st line
are certificates that have been checked and issued by an independent certification body that is supervised by an Accreditation Council in the country where it is located and are “yes/no” certificates or ecolabels (meaning they can not have a variable score per certified organization). The 1st line certificates and ecolabels are automatically checked on validity and scope after uploading and the organization immediately sees their already covered KPI’s in the GSES scorecard pillar reports, and assessment feature.
2nd line
are certificates that can be submitted by the organization itself that have not been independently audited by a certification body/institution, and / or certifications, ecolabels and reports that are not “yes/no” (meaning they can have a variable score per certified organization). The 2nd line reports, certificates and ecolabels are then double checked by an independent data audit after uploading the (audit) report and proof of certification, this can take up to a maximum of 5 working days.
THE gSes system
Why we created the Meta Standard and GSES benchmark
A lot of companies and public organisations are struggling to be more sustainable, to identify the definition of sustainability, and to really make an impact. With a crowded landscape of certifications, norms, guidelines, regulations and labels, the term ‘sustainability’ has become increasingly amorphous, with various definitions that make it difficult to pinpoint what someone is actually talking about when they talk about sustainability. GSES is a groundbreaking effort to solve this problem, allowing for meaningful impact by creating a universal, accessible and actionable language of sustainability.
Why do organizations use the meta standard and benchmark?
- Measuring, monitoring and verifying the organization itself
- Measuring, monitoring and verifying the suppliers
- Measuring, monitoring and verifying the products
- Measuring, monitoring and verifying the clients
- Measuring, monitoring and verifying the assets
- Measuring, monitoring and verifying the organizations events
- Measuring based on verified data - supply chains , client cases etc
- Measuring within days instead of years
- Insights based on verified data sources calculated through the GSES Meta Standard
You can use these features per module and select the modules you need. Organizations can thus standardize the definition of sustainability across all levels of your organization. At the same time, organizations can fast-track their compliance with laws and regulations by leveraging GSES.
The House of Sustainability pillars
The Global Sustainable Meta Standard and its underlying pillar assessments consist of several components that together form the ‘House of Sustainability’. This model shows how our multi-level, holistic approach works. The Global Sustainable Meta Standard measures organizations, their supply chain companies and their products on two levels combined covering all facets of sustainability:
Each pillar of the House can be measured, verified and certified separately. All components together enable the organization to take steps towards socially responsible and sustainable entrepreneurship, while at the same time contributing to the realization of the UN Sustainable Development Goals.
Global Sustainable Enterprise Standard
(GSES pillar benchmark assessments)
Global Sustainable Footprint Standard Nature Impact Rating
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) based on ISO 26000
- Sustainable Procurement (SP) based on ISO 20400
- CO2 Reduction (CO2) based on ISO 50001 & GhG
- Circular Economy (CE) Based on ISO 59000
- Health & Safety (HS) based on ISO 45001
- Biodiversity (BD) based on UNDP
The four pillars on the product level (the ‘Global Sustainable Footprint Standard’) are:
- Environmental Footprint
- Health Footprint
- Circular Footprint
- Social Footprint (based on the CSR pillar on the organizational level).
The GSES House of Sustainability
Our pillars
All the GSES pillars are structured based on the ISO High Level Structure and the Plan, Do, Check, Act philosophy.
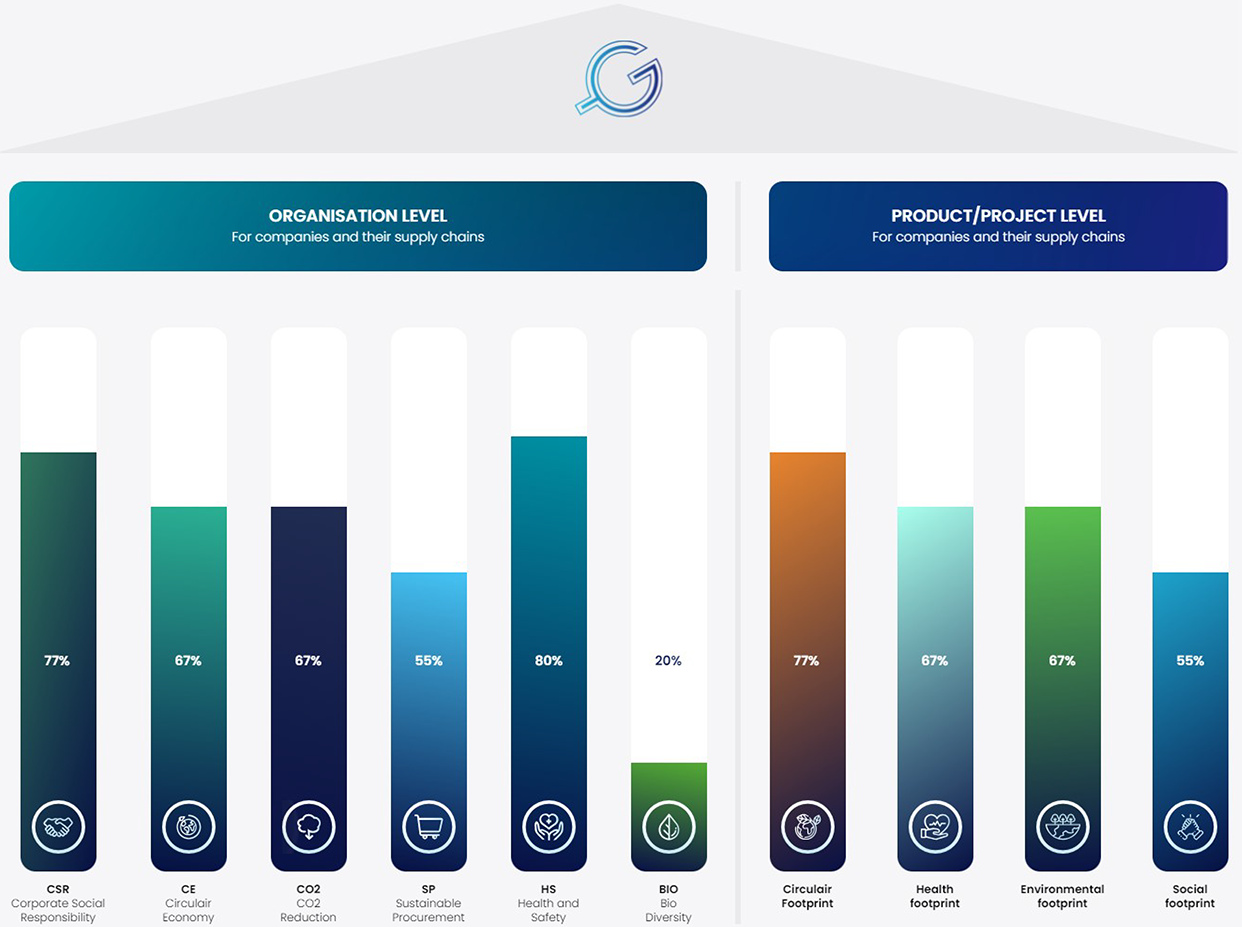

Organisation level
Product/project level
Corporate Social Responsibility
Circulair Economy
CO2 Reduction
Sustainable Procurement
Health and Safety
Bio
Diversity
For companies and their supply chains
ORGANISATION LEVEL
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Circular
Economy (CE)
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Sustainable Procurement (SP)
The Sustainable Procurement (SP) or Socially Responsible Procurement (SRP) pillar from GSE Standard is based is based on the ISO 20400. SP is a theme that plays a prominent role in organizations that develop and implement a sustainable strategy.
Health and Safety (HS)
The GSE-Standard Health & Safety (HS) pillar is based on the international standard ISO 45001:2018 ‘Occupational health and safety management systems – Requirements with guidance for use’.
Biodiversity (BIO)
The GSE-Standard for Bio-Diversity is based on the UN Guidance Note on Standard 1: Biodiversity Conservation and Sustainable Natural Resource Management. As yet, there are no internationally accepted certifiable standards available for managing biodiversity on the organizational level, comparable to ISO standards.
For companies and their supply chains
PRODUCT - PROJECT LEVEL
Circular Footprint (CF)
The Circular Footprint (CF) is part of the GSES Sustainable Product Footprint certification scheme. The CF is based on existing standards such as the Material Circularity Indicator (MCI) of the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, the Material Reutilization ratio of Cradle to Cradle and the detachability index of the Dutch Green Building Council.
Health Footprint (HF)
The Health Footprint (HF) is a component of the GSES Sustainable Product Footprint certification. This footprint enables an assessment of risks of toxic substances associated with a product and its production process.
Environmental Footprint (EF)
The Environmental Footprint (EF) is part of the GSES Sustainable Product Footprint certification. The EF is based on existing life cycle assessment (LCA) standards: ISO14040, ISO14044, PEF, ISO14025 and EN15804. GSES has made some additions that have made the EF into a certifiable standard.
Social Footprint (SF)
Social Footprint is based on the ISO 26000 guideline. The KPI’s attached to a product regarding social claims are independetly verified.
The 17 goals of the 2030 Agenda
SDG Dashboard
SDG Dashboard
The United Nations introduced the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) within the framework of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, which garnered adoption by UN Member States in 2015.
